Contents
混叠现象发生的细节
Nyquist theorem
由于奈奎斯特定理,若音频的采样率为
Aliasing phenomenon
如果有一个信号频率为
最后得到的信号频率为
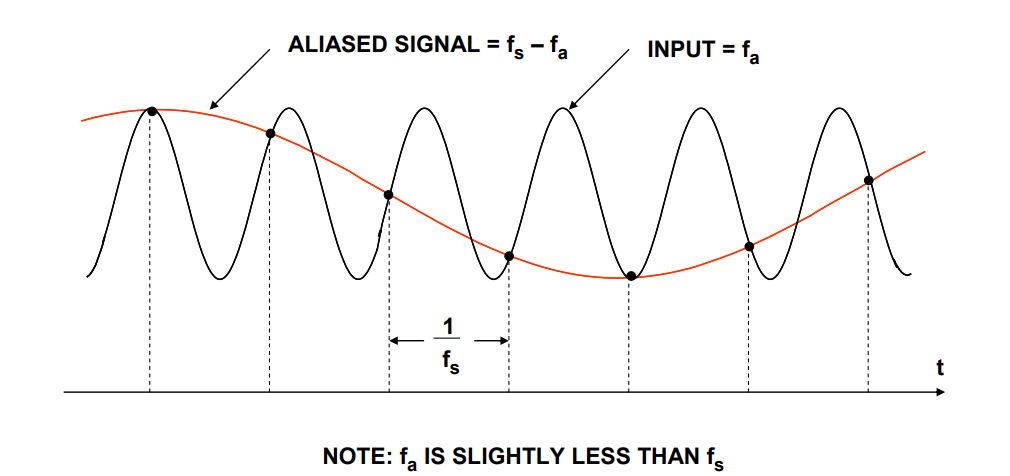
这就是混叠现象。
例如使用10000hz的采样率采样4000hz的信号,得到6000hz的信号。
因此,降采样时,必须先通过低通滤波器。例如,降采样到16000hz,需要通过8000hz滤波器。
细节参考:
Theory of Ideal Bandlimited Interpolation
Sinc functions of finite zero-crossings
下面的是理想的低通滤波器,8000hz。
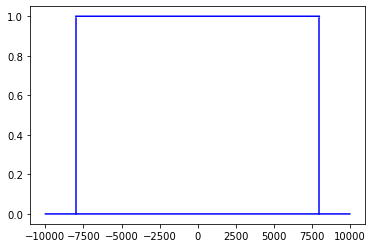
理想的sinc函数有无限个零点,实际使用的时候,使用近似版,即有限个零点,通过规定零点个数来确定近似的精度。
细节如下:
下面看看混叠到底如何发生。
橙色线为8000hz位置,下面是原点左右各8个零点的近似滤波器(kaiser窗)。
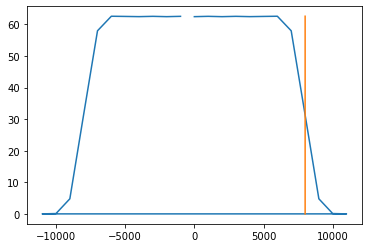
8000-10000hz混叠到6000-8000hz。
下面是左右大概40个零点。

混叠现象发生在7500-8000.
librosa默认参数为‘kaiser_best’,即64 zero-crossings.
Kaldi suggests around 4 to 10 for normal use.
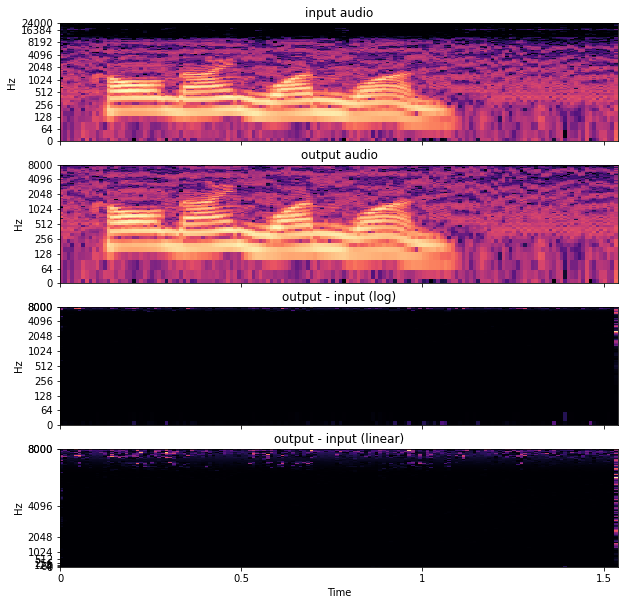
Experiment
控制扰动的SNR为20db,然后最大化输出的MFCC差异,使用的重采样函数为resampling function.
原音频:
nonideal_lowpass_filter/911.wav
输入音频(生成的):
nonideal_lowpass_filter/attack_filter_width4.wav
输出音频:
nonideal_lowpass_filter/attack_output_filter_width4.wav
使用4个零点(左右各4个),改变只在6000-8000hz